- Ethical Hacking Statement
- The Modern Security Operations Center
- The Windows Operating System
- Linux Basics
- Network Protocols
- Ethernet and IP Protocol
- Connectivity Verification
- Address Resolution Protocol
- The Transport Layer
- Network Services
- Network Communication Devices
- Network Security Infrastructure
- Attackers and Their Tools
- Common Threats and Attacks
- Network Monitoring and Tools
- Attacking the Foundation
- Attacking What We Do
- Understanding Defense
- Access Control
- Threat Intelligence
- Public Key Cryptography
- EndPoint Protection
- Endpoint Vulnerability
- Technologies and Protocols
- Network Security Data
- Evaluating Alerts
- Working with Network Security Data
- Digital Forensics and Incidents Analysis and response
1. Which two characteristics describe Ethernet technology? (Choose two.)
- A. It uses a ring topology
- B. It uses the CSMA/CD access control method
- C. It typically uses an average of 16 Mb/s for data transfer rates
- D. It is supported by IEEE 802.3 standards
- E. It is supported by IEEE 802.5 standards
The 802.3 Ethernet standard specifies that a network implement the CSMA/CD
access control method.
2. What are two services provided by the OSI network layer? (Choose two.)
- A. Routing packets toward the destination
- B. Encapsulating PDUs from the transport layer
- C. Performing error detection
- D. Placement of frames on the media
- E. Collision detection
The OSI network layer provides several services to allow communication between
devices:
- Addressing
- Encapsulation
- Routing
- de-encapsulation
Error detection, placing frames on the media, and collision detection are all functions of the data ink layer.
3. How do hosts ensure that their packets are directed to the correct network destination?
- A. They search in their own local routing table for a route to the network destination address and pass this information to the default gateway
- B. They always direct their packets to the default gateway, which will be responsible for the packet delivery
- C. They send a query packet to the default gateway asking for the best route
- D. They have to keep their own local routing table that contains a route to the loopback interface, a local network route, and a remote default route
Hosts must maintain their own local routing table to ensure that network layer
packets are directed to the correct destination network. This local table typically contains a route
to the loopback interface, a route to the network that the host is connected to, and a local default
route, which represents the route that packets must take to reach all remote network addresses.4.
4. A technician uses the ping 127.0.0.1 command. What is the technician testing?
- A. Physical connectivity of a particular PC and the network
- B. the TCP/IP stack on a network host
- C. connectivity between two PCs on the same network
- D. connectivity between two adjacent Cisco device
- E. connectivity between two adjacent Cisco device
127.0.0.1 is the local loopback address on any TCP/IP network device. By pinging
this address, the technician is verifying the TCP/IP protocol stack on that particular device.
5. What is the correct compressed format of the IPv6 address 2001:0db8:eeff:000a:0000:0000:0000:0001?
- A. 2001:db8:eeff:a::0001
- B. 2001:db8:eeff:a::1
- C. 2001:db8:eeff:a:::1
- D. 2001:db8:eeff:a:1
There are two rules for IPv6 address compression. Rule 1: leading zeros in any
hextet can be removed. Rule 2: contiguous hextets of all zeros can be compressed to a double
colon. Rule two can only be applied once.
6. Which function or operation is performed by the LLC sublayer?
- A. It adds a header and trailer to a packet to form an OSL Layer 2 PDU
- B. It communicates with upper protocol layers
- C. It is responsible for media access control
- D. It performs data encapsulation
The Ethernet LLC sublayer has the responsibility to handle communication
between the upper layers and the lower layers of the protocol stack. The LLC is implemented in software and communicates with the upper layers of the application to transition the packet to the lower layers for delivery.
7. How many usable IP addresses are available on the 192.168.1.0/27 network?
- A. 254
- B. 32
- C. 256
- D. 30
- E. 16
A /27 mask is the same as 255.255.255.224. This leaves 5 host bits. With 5 host
bits, 32 IP addresses are possible, but one address represents the subnet number and one address
represents the broadcast address. Thus, 30 addresses can then be used to assign to network
devices.
8. Refer to the exhibit. Consider the IP address configuration shown from PC1. What is a description of the default gateway address?
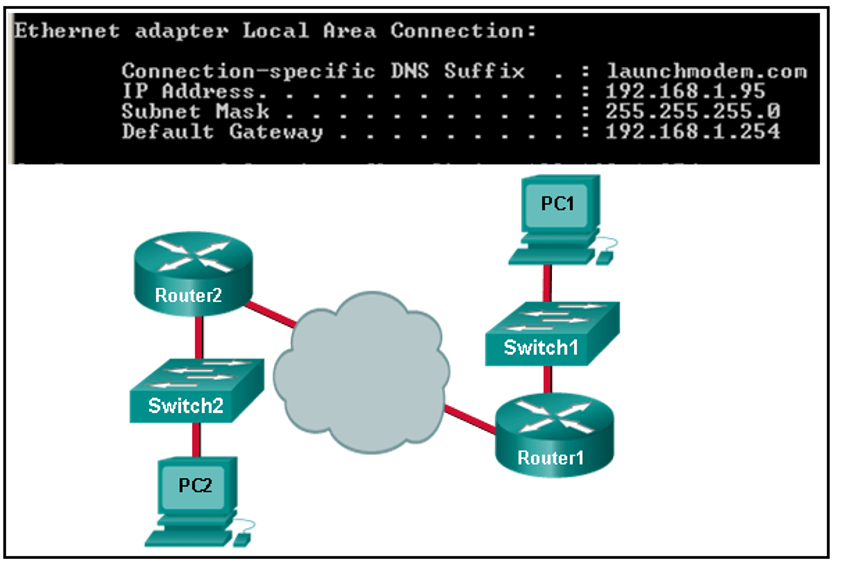
- A. It is the IP address of the router interface that connects the company to the Internet
- B. It is the IP address of the ISP network device located in the cloud
- C. It is the IP address of Switch1 that connects PC1 to other devices on the same LAN
- D. It is the IP address of the Router1 interface that connects the PC1 LAN to Router1
The default gateway is used to route packets destined for remote networks. The
default gateway IP address is the address of the first Layer 3 device (the router interface) that
connects to the same network.
9. What is the command netstat -r used for?
- A. To release the assigned IP address
- B. To renew the default gateway
- C. To display the host routing table
- D. to display the TCP sockets
The command netstat -r displays the host routing table to verify the routes and
costs that a computer uses to communicate to certain networks.
10. A device has an IPv6 address of 2001:0DB8:75a3:0214:0607:1234:aa10:ba01 /64. What is the host identifier of the device?
- A. 0607:1234:aa10:ba01
- B. ba01
- C. 2001:0DB8:75a3
- D. 2001:0DB8
An IPv6 address is made up of 128 bits that are represented as eight blocks of four
hexadecimal digits that are called hextets. Because each hexadecimal digit represents four bits, each hextet represents 16 bits. The /64 network prefix indicates that the first 64 bits, or first four hextets, represent the network portion of the address. Because there are 128 bits in an IPv6
address, this leaves the last 64 bits, or last four hextets, to represent the host identifier. The value for the last four hextets is 0607:1234:aa10:ba01.
11. Which statement describes a MAC address?
- A.It is a physical address assigned to an Ethernet NIC by the manufacturer
- B. It is 128-bits in length
- C. It contains two portions, the network portion and the host portion
- D. It identifies the source and destination addresses of hosts on the Internet
The Media Access Control (MAC) address is a physical address assigned to each
Ethernet NIC by manufacturers. It is 48-bits in length. The MAC address is used to identify the
source and destination on a local Ethernet network. It cannot be routed to remote networks.
12. Why does a Layer 3 device perform the ANDing process on a destination IP address and subnet mask?
- A. To identify the host address of the destination host
- B. To identify faulty frames
- C. To identify the broadcast address of the destination network
- D. To identify the network address of the destination network
ANDing allows us to identify the network address from the IP address and the
network mask.
13. What are two characteristics of IP? (Choose two)
- A. Does not require a dedicated end-to-end connection
- B. Re-assembles out of order packets into the correct order at the receiver end
- C. Guarantees delivery of packets
- D. Retransmits packets if errors occur
- E. Operates independently of the network media
The Internet Protocol (IP) is a connectionless, best effort protocol. This means that
IP requires no end-to-end connection nor does it guarantee delivery of packets. IP is also media independent, which means it operates independently of the network media carrying the packets.
14. Which three IP addresses are private ? (Choose three.)
- A. 172.16.4.4
- B. 172.32.5.2
- C. 192.168.5.5
- D. 224.6.6.6
- E. 192.167.10.10
- F. 10.1.1.1
The private IP addresses are within these three ranges: 10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255,
172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255, 192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255.
