- CCNA Interview Questions [1]
- CCNA Interview Questions [2]
- CCNA Interview Questions [3]
- CCNA Interview Questions [4]
- CCNA Interview Questions [5]
- CCNA Interview Questions [6]
- CCNA Interview Questions [7]
- CCNA Interview Questions[8]
- CCNA Interview Questions [9]
- CCNA Interview Questions [10]
- CCNA Interview Questions [11]
- CCNA Interview Questions [12]
- CCNA Interview Questions [13]
- CCNA Interview Questions [14]
- CCNA Interview Questions [15]
- CCNA Interview Questions [16]

CCNA Interview Questions and Answers -14
1. Explain dynamic desirable & dynamic auto?
Dynamic Desirable – It Initiates negotiation. Switch port configured as DTP dynamic desirable mode will actively try to convert the link to a trunk link if the port connected to other port is capable to form a trunk.
Dynamic Auto – It does not Initiates negotiation but can respond to negotiation. Switch port configured as DTP dynamic auto is capable to form trunk link if the other side switch interface is configured to form a trunk interface and can negotiate with trunk using DTP.
2. What is STP?
3. Who developed STP?
– Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is based on an algorithm, which was developed by Radia Perlman at DEC (Digital Equipment Corporation, now part of HP).
– The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) was then standardized by IEEE as IEEE 802.1D.
4. How does STP maintain a loop-free network?
5. What is Bridge Protocol Data Unit (BPDU) frame?
• The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) enabled switches in a redundant Local Area Network (LAN) need to exchange information between each other for Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) to work properly.
• Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs) are messages exchanged between the switches inside an interconnected redundant Local Area Network (LAN).
• Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs) frames contain information regarding the Switch ID, originating switch port, MAC address, switch port priority, switch port cost etc.
• When Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs) are received, the Switch uses a mathematical formula called the Spanning Tree Algorithm (STA) to know when there is a Layer2 Switch loop in network and determines which of the redundant ports needs to be shut down.
6. What is the destination MAC address used by Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs)?
Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs) frames are sent out as multicast messages regularly at multicast destination MAC address 01:80:c2:00:00:00.
7. What are the different types of BPDUs?
Three types of Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs) are
1. Configuration BPDU (CBPDU),
2. Topology Change Notification (TCN) BPDU
3. Topology Change Notification Acknowledgment (TCA) BPDU
8. What is the basic purpose of the BPDUs and STA?
The basic purpose of the Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs) and the Spanning Tree Algorithm (STA) is to avoid Layer2 Switching loops and Broadcast storms.
9. What is Switch Priority Value (Bridge Priority)?
• Every Switch Participating in a Spanning Tree Protocol network is assigned with a numerical value called Switch Priority Value.
• Switch Priority Value is a 16-bit binary number.
• The Switch Priority, which is a numerical value defined by IEEE 802.1D, which is equal to 32,768 by default.
• Switch Priority value decides which Switch can become Root Bridge (Root Switch).
• The Switch Priority value is used to find the Switch ID.
10. What is Switch ID (Bridge ID)?
• Switch ID decides which Switch can become Root Switch. A Switch with lowest Switch ID will become the Root Switch.
The Switch ID (Bridge ID) is made from two values.
• The Switch Priority which is a numerical value defined by IEEE 802.1D, which is equal to 32,768 by default.
• The MAC Address of the Switch.
11. What is Root Switch (Root Bridge)?
The main function of the root switch is to broadcast network topology changes to all the switches in the network.
• When a switch detects a topology change (i.e., a trunk goes down) it sends a topology change notification (TCN) BPDU to the root switch. The root switch then broadcasts that topology change out to the other switches.
12. How Root bridge is elected?
The bridge ID is used to elect the root bridge in the STP domain. This ID is 8 bytes long and includes both the priority and the MAC address of the device.
Switch with the lowest Bridge ID is elected as the Root bridge which means Switch with the lowest priority will become Root Bridge if two or more switches have same priority than switch with lowest mac address will become Root Bridge.
13. What are STP Timers and Explain different types of STP Timers?
STP uses three timers to make sure that a network converges properly before a bridging loop can form.
Hello timer – The time interval between Configuration BPDUs sent by the root bridge. It is 2 seconds by default.
Forward Delay timer – The time interval that a switch port spends in both the Listening and Learning states. The default value is 15 seconds.
Max (Maximum) Age timer – Maximum length of time a BPDU can be stored without receiving an update. It can also be define as a time interval that a switch stores a BPDU before discarding it. It is 20 seconds by default.
14. What are the different port states?
1.Disabled – A port in the disabled state does not participate in the STP.
2.Blocking – A blocked port does not forward frames. It only listens to BPDUs. The purpose of the blocking state is to prevent the use of looped paths.
3.Listening – A port in listening state prepares to forward data frames without populating the MAC address table. The port also sends and listens to BPDUs to make sure no loops occur on the network.
4.Learning – A port in learning state populates the MAC address table but doesn’t forward data frames. The port still sends and receives BPDUs as before.
5.Forwarding – The port now can send and receive data frames, collect MAC addresses in its address table, send and receive BPDUs. The port is now a fully functioning switch port within the spanning-tree topology.
15. Explain types of STP Port Roles?
Root port – The root port is always the link directly connected to the root bridge, or the shortest path to the root bridge. It is always on Non-Root Bridge.
Designated port – A designated port is one that has been determined as having the best (lowest) cost. A designated port will be marked as a forwarding port. It can be on both Root Bridge & Non Root Bridge. All ports of Root Bridge are Designated Port.
Alternate port – A blocked port is the port that is used to prevent loops. It only listens to BPDUs. Any port other than Root port & designated port is a Block Port.
16. What is Extended System ID?
The Extended System ID is utilized by spanning-tree to include the VLAN ID information inside 16-bit STP Bridge Priority value. Extended System ID is the least significant 12-bits in 16-bit STP Bridge Priority value.
17. What is Path Cost or Spanning Tree Path Cost value?
The Spanning Tree Cost Value is inversely proportional to the bandwidth of the link and therefore a path with a low cost value is more preferable than a path with high cost value.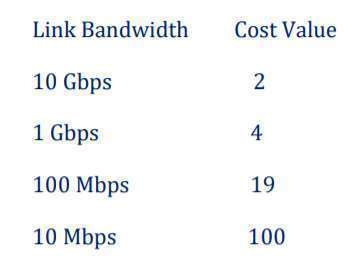
18. Why spanning tree BPDU filter is used?
BPDU filter is a feature used to filter sending or receiving BPDUs on a switchport. … Enabling BPDU filtering in the interface level stops sending or receiving BPDU on this interface.
19. Explain store and forward Layer 2 Forwarding.
Store-and-forward switching is one of three primary types of LAN switching. With the store-andforward switching method, the LAN switch copies the entire frame onto its onboard buffers and computes the cyclic redundancy check (CRC). Because it copies the entire frame, latency through the switch varies with frame length.
The frame is discarded if it contains a CRC error, if it’s too short (less than 64 bytes including the CRC), or if it’s too long (more than 1,518 bytes including the CRC). If the frame doesn’t contain any errors, the LAN switch looks up the destination hardware address in its forwarding or switching table and determines the outgoing interface. It then forwards the frame toward its destination.
20. What is PVST or PVST+?
Per-VLAN spanning tree protocol plus (PVST+) is a Cisco proprietary protocol that expands on the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) by allowing a separate spanning tree for each VLAN.
Cisco first developed this protocol as PVST, which worked with the Cisco ISL trunking protocol, andthen later developed PVST+ which utilizes the 802.1Q trunking protocol.
21. What is the working of PVST or PVST+?
By creating a separate spanning tree for each VLAN, data traffic from the different VLANs can take different paths across the network, as opposed to all switched traffic taking the same path. This can effectively create a load balancing situation and improve network efficiency.
By default the Cisco switches in Packet Tracer appear to be using PVST+ as the default implementation of spanning tree protocol.
22. What is RSTP?
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) is an enhancement of the original STP 802.1D protocol. The RSTP 802.1w protocol is an IEEE open implementation.
23. What is Rapid-PVST+?
Cisco has its own proprietary implementation of RSTP, that includes the benefits of its Per-VLAN spanning tree protocols, called Rapid-PVST+.
24. What is the working of RSTP and Rapid-PVST+?
Rapid-PVST+ and RSTP are important enhancements to the original STP protocol because they can switch ports from blocking to forwarding without relying on timers, execute spanning tree calculations and converge the network faster than STP.
In STP, network convergence can take up to 50 seconds, with RSTP and Rapid-PVST+ network convergence can happen in just over 6 seconds.
Points to remember-
– STP is also called IEEE 802.1D
– STP is used to avoid loops
– Ethernet has no capacity for detecting loops.If a loop exist,broadcast storm will appear
– STP prevents loop formation by detecting redundant links and disabling them until needed.
– STP is enabled by default in switches
– STP works by selecting a switch in the network as a root bridge
– A STP network must select
o One root bridge
o One root port per non-root bridge
o One designated port per network segment
– Designated port (DP) : All ports in root bridge must be DP.All designated ports will be in forwarding state
– Root Port (RP) : Root port is the port in the non-root bridge that connects the best path to root bridge
– Blocked port (BP) : Such ports will be in blocked state.it will receive informations from Designated ports but will not send any information through it
– One end of every link must be designated port.Other end may be Blocked Port OR Root Port
25. What is Loop Guard?
Loop Guard keeps track of the BPDU activity on non-designated ports. It does not allow nondesignated ports to become designated ports in case of sudden loss of BPDUs. While BPDUs are received, the port is allowed to behave normally. When BPDUs go missing, Loop Guard moves the port into the loop-inconsistent state (port is effectively blocking at this point to prevent a loop from forming and to keep it in the non-designated role). When BPDUs are received on the port again, Loop Guard allows the port to move through the normal STP states and become active.
It can be enabled on both interface & global level. It affects per vlan basis.
Switch(config)# spanning-tree loopguard default
Switch(config-if)# spanning-tree guard loop
26. What is SVI?
A Switched Virtual Interface (SVI) is a virtual LAN (VLAN) of switch ports represented by one interface to a routing or bridging system. There is no physical interface for the VLAN and the SVI provides the Layer 3 processing for packets from all switch ports associated with the VLAN.
27. Which switching technology reduces the size of a broadcast domain?
VLAN’s [virtual LAN’s ]
28. what is meant by “router on stick”?
Router-on-a-stick is a term frequently used to describe a setup up that consists of a router and switch connected using one Ethernet link configured as an 802.1q trunk link. In this setup, the switch is configured with multiple VLANs and the router performs all routing between the different networks/VLANs.
29. which is the default mode in switch ports?
Dynamic Auto
30. On a multilayer Catalyst switch, which interface command is used to convert a Layer 3 interface to a Layer 2 interface?
Switch (config-if)# switchport
